小麦细胞壁转化酶基因 Genome-level identification of cell wall invertase genes in wheat for the study of drought tolerance
小麦细胞壁转化酶基因(Genome-level identification of cell wall invertase genes in wheat for the study of drought tolerance)
2012/07/12 21:28:37
Genome-level identification of cell wall invertase genes in wheat for the study of drought tolerance
Hollie Webster, Gabriel Keeble, Bernard Dell, John Fosu-Nyarko, Y. Mukai, Paula Moolhuijzen, Matthew Bellgard, Jizeng Jia, Xiuying Kong, Catherine Feuillet, Frédéric Choulet, International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium and Rudi Appels
Functional Plant Biology 39(7) 569-579
doi: 10.1071/FP12083
In wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) drought-induced pollen sterility is a major contributor to grain yield loss and is caused by the downregulation of the cell wall invertase gene IVR1. The IVR1 gene catalyses the irreversible hydrolysis of sucrose to glucose and fructose, the essential energy substrates which support pollen development. Downregulation of IVR1 in response to drought is isoform specific and shows variation in temporal and tissue-specific expression. IVR1 is now prompting interest as a candidate gene for molecular marker development to screen wheat germplasm for improved drought tolerance. The aim of this study was to define the family of IVR1 genes to enable: (1) individual isoforms to be assayed in gene expression studies; and (2) greater accuracy in IVR1 mapping to the wheat genetic map and drought tolerance QTL analysis. Using a cell wall invertase-specific motif as a probe, wheat genomics platforms were screened for the presence of unidentified IVR1 isoforms. Wheat genomics platforms screened included the IWGSC wheat survey sequence, the wheat D genome donor sequence from Aegilops tauschii Coss, and the CCG wheat chromosome 3B assembly: contig506. Chromosome-specific sequences homologous to the query motif were isolated and characterised. Sequence annotation results showed five previously unidentified IVR1 isoforms exist on multiple chromosome arms and on all three genomes (A, B and D): IVR1–3A, IVR1–4A, IVR1–5B, IVR1.2–3B and IVR1-5D. Including three previously characterised IVR1 isoforms (IVR1.1–1A, IVR1.2–1A and IVR1.1–3B), the total number of isoform gene family members is eight. The IVR1 isoforms contain two motifs common to cell wall invertase (NDPN and WECPDF) and a high degree of conservation in exon 4, suggesting conservation of functionality. Sequence divergence at a primary structure level in other regions of the gene was evident amongst the isoforms, which likely contributes to variation in gene regulation and expression in response to water deficit within this subfamily of IVR1 isoforms in wheat.
干旱导致的花粉不育是导致小麦(Triticum aestivum L.)产量损失的主要因素,这是由细胞壁转化酶IVR1基因的下调引起的。IVR1基因催化蔗糖向葡萄糖和果糖的不可逆水解,其产物是花粉发育必需的能量底物。IVR1由干旱诱导的下调具有同工特异性,其表达表现出时间特异与组织特异。现在IVR1作为发掘分子标记的候选基因,筛选小麦种质以促进干旱抗性。本文目的在于定义IVR1基因家族,以便:(1)在基因表达研究中区分各同工型;(2)提高IVR1 mapping到小麦遗传图与干旱抗性QTL分析的准确性。使用一段细胞壁转化酶特异性基序作为探针,在小麦基因组学平台上筛选未阐明的IVR1同工型。筛选过的小麦基因组学平台包括IWGSC wheat survey sequence、the wheat D genome donor sequence from Aegilops tauschii Coss和the CCG wheat chromosome 3B assembly: contig506。与查询基序同源的染色体特异性序列被分离并鉴定。序列注释结果表明在多个染色体臂与所有3个基因组(A、B和D)中存在5个未鉴定过的IVR同工型:IVR1–3A、IVR1–4A、IVR1–5B、IVR1.2–3B和IVR1-5D。如果包括3个以前阐明的IVR1同工型(IVR1.1–1A、IVR1.2–1A和IVR1.1–3B),同工型基因家族成员总数达到8个。IVR1同工型包含两个与细胞壁转化酶(NDPN和WECPDF)相同的基序,在第4外显子高度保守,表明功能性保守。基因其它部分序列歧化明显,这可能与小麦IVR同工型亚家族在缺水应答时基因调节与表达的差异有关系。
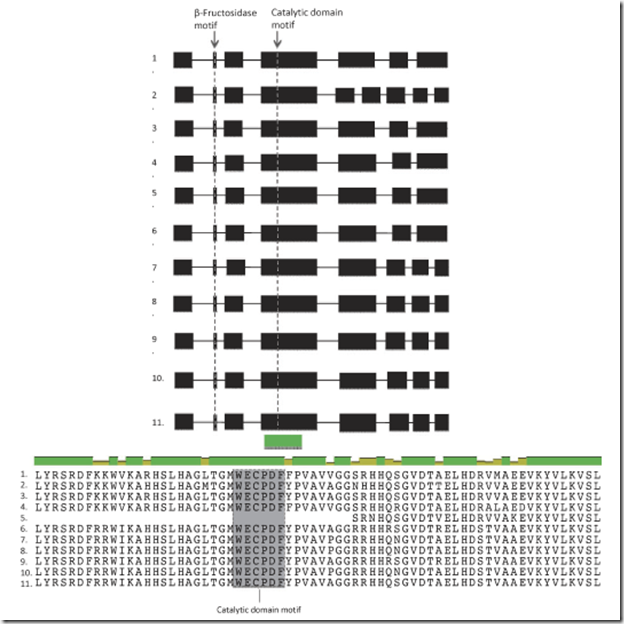
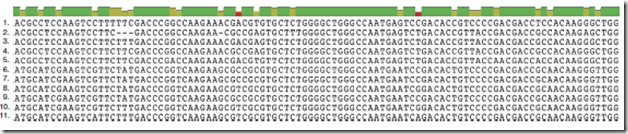
Fig. 5. Comparison of wheat IVR1 isoform nucleotide sequence in exon 4. In the multiple sequence alignment identical, conserved and analogous regions between the various IVR1 isoforms are demarcated by the colour of the line seen above the alignment; where the dark green line represents homology, light olive green represents a high degree of conservation and red represents low conservation.